CSES-01 is a 3-axis attitude stabilized satellite based on the Chinese CAST2000 platform, with a mass of about 750 kg and a peak power consumption of about 900 W. The orbit is Sun-synchronous with 97,4° inclination at an altitude of 507 km. The satellite was launched in orbit on Feb 2nd, 2018 from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in the Gobi Desert (Inner Mongolia).
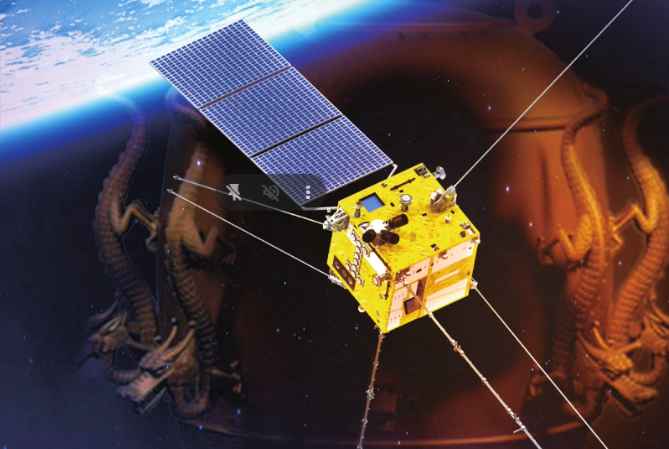

CSES-01 mission is investigating the structure and the dynamics of the topside ionosphere, the coupling mechanisms between upper atmosphere, ionosphere and magnetosphere and the temporal variations of the geomagnetic field, in quiet and disturbed conditions. Data collected by the mission also allow to study solar-terrestrial interactions and phenomena of solar physics, namely Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs), solar flares and cosmic ray solar modulation.
The mission is contributing to develop an observational sharing service for the international cooperation and the scientific community.
CSES-01 carries onboard the following payloads:
in depth

The study of earthquakes from space is an intriguing field that utilizes cutting-edge technology to...
Read more
The near-Earth environment (NEE) is a dynamic region influenced by space weather, which includes solar...
Read more
Space Weather refers to the environmental conditions in space as influenced by the Sun and...
Read moreThe CSES-01 (Chinese Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite), launched on February 2018 and equipped with a large set of instruments, including a High-Energy Particle Detector (HEPD-01), an electric field detector (EFD-01), a flux gate (HPM) and a search-coil (SCM) magnetometer, has had the opportunity to explore the Southern auroral oval region during a time interval characterized by the occurrence of a magnetospheric substorm. During the crossing of the southern auroral region, the satellite has measured simultaneously the magnetic and electric field fluctuations. CSES-01, which has been originally designed to study possible correlations between seismic events and iono/magnetospheric perturbations, flies in the topside of the ionosphere at 500 km of altitude on a Sun-synchronous orbit. Thus, it also provided the opportunity to explore the plasma dynamics at an altitude higher than that at which the typical auroral phenomena occur.

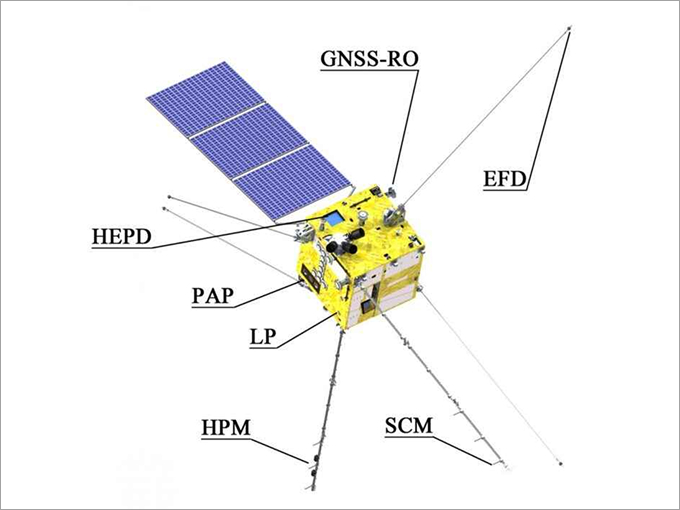
| Category | Payload Name | Observation Target |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Particle | High Energy Particle Detector (HEPD) | Proton: 30 Mev ~ 200 Mev Electron: 3 ~ 100 Mev |
| High Energy Particle Detector (HEPD) | Electron: 25 KeV ~ 3.2 MeV | |
| Electro-Magnetic Field | Electric Field Detectors (EFD) | Electric Field DC ~ 3.5 MHz |
| High Precision Magnetometer (HPM) • Vector Magnetic Field: FGM1, FMG2. • Scalar Magnetic Field: CDSM, CPT. |
Magnetic Field: 10 Hz ~ 20 kHz | |
| Search Coil Magnetometer (SCM) | Magnetic Field: 10 Hz ~ 20 kHz | |
| In Situ Plasma | Plasma Analyzer Package (PAP) |
Composition: H+, He+, O+ Ni: 5×10² ~ 1×10⁷ cm⁻³ Ti: 500K ~ 10000 cm⁻³ |
| Langmuir Probe (LP) |
Ni: 5×10² ~ 1×10⁷ cm⁻³ Ti: 500K ~ 10000 cm⁻³ |
|
| Plasma Profile Construction | GNSS Occultation Receiver | TEC by transmit VH/U/L Signal |
| Tri-Band Beacon | TEC by transmit VH/U/L Signal | |
| Ionospheric | O₂ 135.6 nm and N₂ LBH airglow |